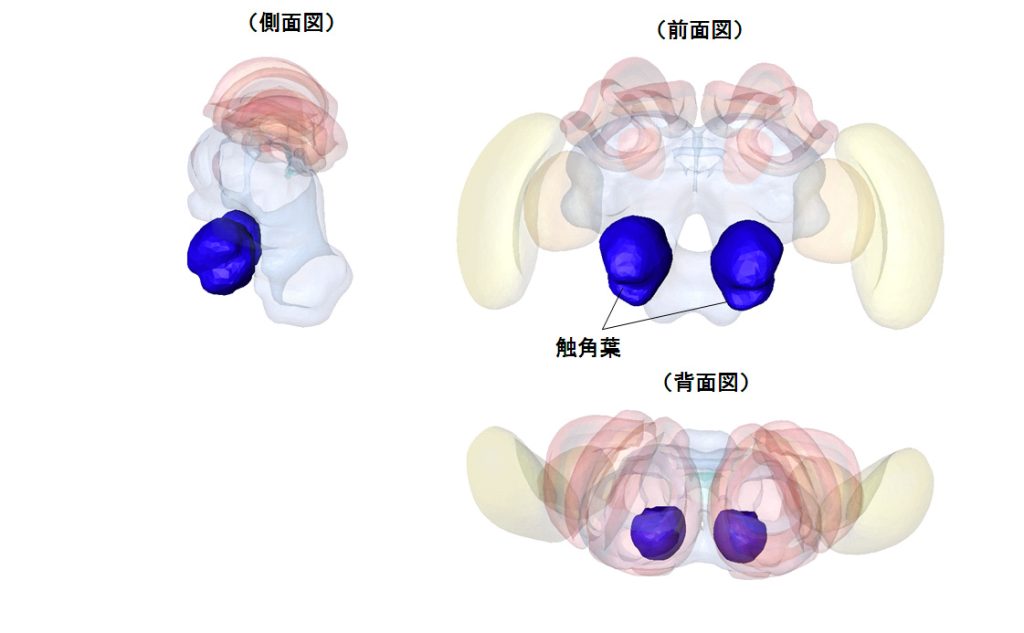
1.構造働き蜂の触角葉は,約160個の糸球体を持ち(Galizia et al., 1999),触角神経の逆行性染色によって,触角葉内の嗅受容細胞の通る神経路を元にグループ化され,グループ内で一意に糸球体を同定する形態学的な手法が確立されている.
2.機能
触角葉の神経回路は,他の昆虫と同様匂い識別に必要である.Stopferらは主要な抑制性神経伝達物質GABAの受容体の阻害剤を用いることで,触角葉の処理が匂い識別に重要な役割を起こすことを示している(Stopfer et al., 1997).抑制性伝達を阻害することによって,物理化学的な特性が大幅に異なる匂いの識別は可能であるが,似た匂いの識別ができなくなることから,触角葉内の抑制性伝達による処理が,匂いのファインチューニングに必要であると結論してる.
単一細胞レベルにおいては,急性および培養単離細胞で,細胞体の膜の電気的性質および薬理学的プロファイルが研究されている(嗅受容細胞,Laurent et al., 2002; 中枢神経細胞,Grünewald 2003; Barbara et al., 2005).
3.神経回路
3-1.嗅受容細胞
単一感覚子の中に異なるタイプの嗅受容細胞を有する(Kelber et al., 2006).
3-2.投射神経
細胞内記録法によって,投射神経の形態,匂い応答が分析されており,内側と外側の神経路を走行する投射神経の匂い応答はそれぞれ異なることなどが明らかになっている(Abel et al., 2001; Müller et al., 2002; Krofczik et al., 2008).
3-3.局所介在神経
局所介在神経の単一細胞レベルの応答が分析されている(Iwama and Shibuya, 1998).GABA受容体の阻害剤を用いたカルシウムイメージング実験によって,局所介在神経の抑制作用によって,投射神経の活動が修飾されることが明らかになっている(Sachse and Galizia, 2002).Linsterらは触角葉の神経回路モデルを構築し,カルシウムイメージングによる,嗅受容細胞の匂い応答データを入力として,投射神経の活動パターンを最もよく再現する糸球体間の接続関係は,嗅受容細胞の匂い応答プロファイルのよく似た糸球体をより強く結合させるものであることを,計算機シミュレーションによって確認し,ヘテロタイプの局所介在神経がこうした機能を持つのではないかと推測している(Linster et al., 2005).
3-4.神経集団活動
ミツバチの触角葉では昆虫で初めてカルシウムイメージング法が適用され(Jorege et al., 1997; Galizia et al., 1997),表面の糸球体群については,嗅受容細胞および投射神経の匂い応答プロファイルが明らかにされ,データベースとして整備されている(http://neuro.uni-konstanz.de/).ミツバチの吻伸展反射学習の実験系における匂いの汎化を元にして,ミツバチの知覚している匂い空間を行動レベルで求めたところ,触角葉における糸球体の神経活動パターンとよく相関することが分かっている(Guerriei et al., 2005).直鎖脂肪族化合物の炭素鎖長が異なると,活動する糸球体が空間的に連続的に変化し(Galizia et al., 1999),匂いの入力強度依存的に,糸球体の活動領域は増大する(Sachse et al., 2003).また,投射神経の自発活動が,以前に受容した刺激の履歴によっても変化することが分かっている(Galan et al., 2006).
4.神経伝達物質・神経修飾物質
ミツバチの触角葉内には,アセチルコリン,GABA,ヒスタミン,オクトパミン,セロトニン,アラトスタチン等が存在する(Mercer et al., 1983; Kreissl and Bicker, 1989; Rybak and Eichmüller, 1993; Kreissl et al., 2010).匂いの学習にオクトパミンが寄与し(Hammer et al., 1993),オクトパミンは触角葉内のタンパクキナーゼAを活性化させる(Hildebrandt and Müller, 1995).また,匂いを学習することによって,触角葉中のタンパクキナーゼCの量が長時間増大することが分かっている(Grünbaum and Müller, 1998).NO-cGMP合成経路を介したタンパクキナーゼAが慣れに関与することが示唆されている(Müller et al., 2002).ヒスタミンも抑制性の神経伝達物質である可能性が指摘されている(Sachse et al., 2006).
5.可塑性
神経活動は羽化後の発達段階によって変化することが分かっている(Wang et al., 2005).発達後も,受容した匂い経験,学習により糸球体構造および神経活動パターンが変化することなどが分かっている(Faber et al., 1999; Brown et al., 2004; Fernandez et al., 2009; Hourcade et al., 2009; Denker et al., 2010).また,味と匂いの連合学習において重要なオクトパミンの存在下で,触角葉の神経活動が変化する(Farooqui et al., 2003).また,特定の神経路を通る投射神経の活動パターンは学習によっても変化しない(Peele et al, 2006).
参考文献
Abel R, Rybak J, Menzel R. Structure and response patterns of olfactory interneurons in the honeybee, Apis mellifera. J Comp Neurol. 2001 437(3):363-83.
Barbara GS, Zube C, Rybak J, Gauthier M, Grünewald B. Acetylcholine, GABA and glutamate induce ionic currents in cultured antennal lobe neurons of the honeybee, Apis mellifera. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2005 191(9):823-36.
Brown SM, Napper RM, Mercer AR. Foraging experience, glomerulus volume, and synapse number: A stereological study of the honey bee antennal lobe. J Neurobiol. 2004 60(1):40-50.
Denker M, Finke R, Schaupp F, Grün S, Menzel R. Neural correlates of odor learning in the honeybee antennal lobe. Eur J Neurosci. 2010 31(1):119-33.
Faber T, Joerges J, Menzel R. Associative learning modifies neural representations of odors in the insect brain. Nat Neurosci. 1999 2(1):74-8.
Farooqui T, Robinson K, Vaessin H, Smith BH. Modulation of early olfactory processing by an octopaminergic reinforcement pathway in the honeybee. J Neurosci. 2003 23(12):5370-80.
Fernandez PC, Locatelli FF, Person-Rennell N, Deleo G, Smith BH. Associative conditioning tunes transient dynamics of early olfactory processing. J Neurosci. 2009 29(33):10191-202.
Galán RF, Weidert M, Menzel R, Herz AV, Galizia CG. Sensory memory for odors is encoded in spontaneous correlated activity between olfactory glomeruli. Neural Comput. 2006 18(1):10-25.
Galizia CG, Joerges J, Küttner A, Faber T, Menzel R. A semi-in-vivo preparation for optical recording of the insect brain. J Neurosci Methods. 1997 76(1):61-9.
Galizia CG, Kimmerle B. Physiological and morphological characterization of honeybee olfactory neurons combining electrophysiology, calcium imaging and confocal microscopy. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2004 190(1):21-38.
Galizia CG, Küttner A, Joerges J, Menzel R. Odour representation in honeybee olfactory glomeruli shows slow temporal dynamics: an optical recording study using a voltage-sensitive dye. J Insect Physiol. 2000 46(6):877-886.
Galizia CG, McIlwrath SL, Menzel R. A digital three-dimensional atlas of the honeybee antennal lobe based on optical sections acquired by confocal microscopy. Cell Tissue Res. 1999 295(3):383-94.
Galizia CG, Sachse S, Rappert A, Menzel R. The glomerular code for odor representation is species specific in the honeybee Apis mellifera. Nat Neurosci. 1999 2(5):473-8.
Grünbaum L, Müller U. Induction of a specific olfactory memory leads to a long-lasting activation of protein kinase C in the antennal lobe of the honeybee. J Neurosci. 1998 18(11):4384-92.
Grünewald B. Differential expression of voltage-sensitive K+ and Ca2+ currents in neurons of the honeybee olfactory pathway. J Exp Biol. 2003 206(Pt 1):117-29.
Guerrieri F, Schubert M, Sandoz JC, Giurfa M. Perceptual and neural olfactory similarity in honeybees. PLoS Biol. 2005 3(4):e60.
Hammer M (1993) An identified neuron mediates the unconditioned stimulus in associative olfactory learning in honeybees.Nature 366: 59-63
Hildebrandt H, Müller U. Octopamine mediates rapid stimulation of protein kinase A in the antennal lobe of honeybees. J Neurobiol. 1995 27(1):44-50.
Hildebrandt H, Müller U. PKA activity in the antennal lobe of honeybees is regulated by chemosensory stimulation in vivo. Brain Res. 1995 679(2):281-8.
Hourcade B, Perisse E, Devaud JM, Sandoz JC. Long-term memory shapes the primary olfactory center of an insect brain. Learn Mem. 16(10):607-15.
Iwama A, Shibuya T. Physiology and morphology of olfactory neurons associating with the protocerebral lobe of the honeybee brain. J Insect Physiol. 1998 44(12):1191-1204.
Joerges J, Küttner A, Galizia CG, Menzel R (1997) Representations of odour mixtures visualized in the honeybee brain. Nature 387:285-288.
Kelber C, Rössler W, Keineidam CJ. Multiple olfactory receptor neurons and their axonal projections in the antennal lobe of the honeybee Apis mellifera. J Comp Neurol. 2006 496:395-405.
Kreissl S, Bicker G. Histochemistry of acetylcholinesterase and immunocytochemistry of an acetylcholine receptor-like antigen in the brain of the honeybee. J Comp Neurol. 1989 286(1):71-84.
Kreissl S, Eichmüller S, Bicker G, Rapus J, Eckert M. Octopamine-like immunoreactivity in the brain and subesophageal ganglion of the honeybee. J Comp Neurol. 1994 348(4):583-95.
Kreissl S, Strasser Chr, Galizia CG. Allatostatin-immunoreactivity in the honeybee brain. J Comp Neurol. 2010 518:1391-1417.
Krofczik S, Menzel R, Nawrot MP. Rapid odor processing in the honeybee antennal lobe network. Front Comput Neurosci. 2008;2:9.
Laurent S, Masson C, Jakob I. Whole-cell recording from honeybee olfactory receptor neurons: ionic currents, membrane excitability and odourant response in developing workerbee and drone. Eur J Neurosci. 2002 15(7):1139-52.
Linster C, Sachse S, Galizia CG. Computational modeling suggests that response properties rather than spatial position determine connectivity between olfactory glomeruli. J Neurophysiol. 2005 93(6):3410-7.
Mercer AR, Mobbs PG, Davenport AP, Evans PD. Biogenic amines in the brain of the honeybee, Apis mellifera. Cell Tissue Res. 1983 234(3):655-77.
Müller D, Abel R, Brandt R, Zöckler M, Menzel R. Differential parallel processing of olfactory information in the honeybee, Apis mellifera L. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2002 188(5):359-70.
Müller U, Hildebrandt H. Nitric oxide/cGMP-mediated protein kinase A activation in the antennal lobes plays an important role in appetitive reflex habituation in the honeybee. J Neurosci. 2002 22(19):8739-47.
Peele P, Ditzen M, Menzel R, Galizia CG. Appetitive odor learning does not change olfactory coding in a subpopulation of honeybee antennal lobe neurons. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol. 2006 192(10):1083-103.
Rybak J, Eichmüller S. Structural plasticity of an immunochemically identified set of honeybee olfactory interneurones. Acta Biol Hung. 1993 44(1):61-5.
Sachse S, Galizia CG. Role of inhibition for temporal and spatial odor representation in olfactory output neurons: a calcium imaging study. J Neurophysiol. 2002 87(2):1106-17.
Sachse S, Galizia CG. The coding of odour-intensity in the honeybee antennal lobe: local computation optimizes odour representation. Eur J Neurosci. 2003 18(8):2119-32.
Sachse S, Peele P, Silbering AF, Gühmann M, Galizia CG. Role of histamine as a putative inhibitory transmitter in the honeybee antennal lobe. Front Zool. 2006
Stopfer M, Bhagavan S, Smith BH, Laurent G. Impaired odour discrimination on desynchronization of odour-encoding neural assemblies. Nature 390:70-74.
Wang S, Zhang S, Sato K, Srinivasan MV. Maturation of odor representation in the honeybee antennal lobe. J Insect Physiol. 2005 51(11):1244-54.